 Concentration Gradients and
Diffusion:
Concentration Gradients and
Diffusion:  Concentration Gradients and
Diffusion:
Concentration Gradients and
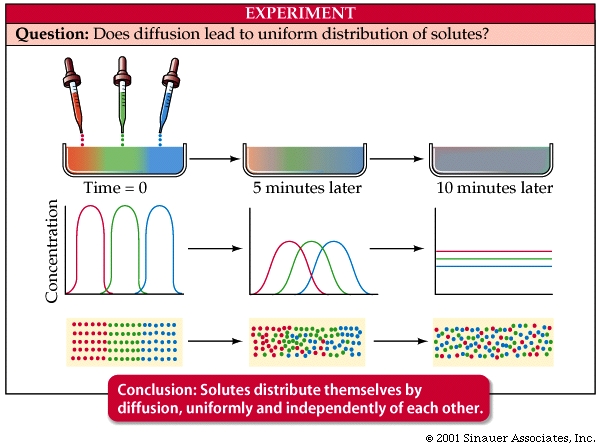
Diffusion: A concentration gradient is a difference in the number of molecules or ions of a given substance between two adjoining regions. Molecules constantly collide and tend to move according to existing concentration gradients.
The net movement of like molecules down a concentration gradient (high to low) is simple diffusion. Gradients in temperature, electric charge, and pressure, can influence movements.
Concentration gradients influence reversible reactions. If the energy content and concentration of the starting substances are high, the reaction will run forward to products. When enough product molecules or ions are available, the reaction tends to run to the reverse. Left to themselves, reversible reactions might reach chemical equilibrium.
REVIEW: In simple diffusion
a. the rate of movement of molecules is controlled by temperature and pressure.
b. the movement of individual molecules is random.
c. the movement of molecules of one substance is independent of the movement of any other
substance.
d. the net movement is away from the region of highest concentration.
e. all of these���
PREVIOUS
NEXT
LECTURE 19 INDEX
MAIN INDEX