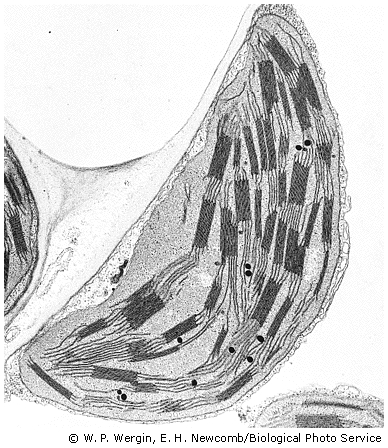

Plant cells may also have chloroplasts or other plastids. Chloroplasts are oval or disk shaped. They are bounded by a double membrane, and are critical to the process of photosynthesis. They have stacked disks (grana), pigments and enzymes which trap sunlight energy to form ATP. Sugars are formed in the fluid substance (stroma) surrounding the stacks. Pigments such as chlorophyll (green) confer distinctive colors to the chloroplasts.
Chromoplasts have carotenoids, which impart red-to-yellow colors to plant parts, but no chlorophyll.
Amyloplasts have no pigments. They store starch grains in plant parts such as potato tubers.
Eukaryotic Cell Walls: Many single-celled eukaryotes have a cell wall. This is a supportive and protective structure outside the plasma membrane. Microscopic pores allow water and solute passage to and from the underlying plasma membrane. In plants, bundles of cellulose strands form the primary cell wall, which is more pliable than the more rigid secondary wall that is laid down inside it later. Plasmodesmata are channels that cross the adjacent walls to connect the cytoplasm of neighboring cells.
REVIEW: What cell organelle is found in plant cells but NOT in animal cells?� �
REVIEW: �Cells of many protistans, plants, and fungi, but not animals, commonly have _____ .�
REVIEW: Four of the five answers listed below are familiar organelles in the cytoplasm. Select the exception.
a. nucleolus
b. mitochondria
c. ribosome
d. Golgi apparatus
e. chloroplast��
PREVIOUS
NEXT
LECTURE 4 INDEX
MAIN INDEX