
The thyroid hormone, thyroxine, is a modified amino acid that contains four atoms of iodine. It accelerates oxidative metabolism throughout the body. An abnormal deficiency of thyroxine causes goiter, decreased heart rate, lethargy, obesity, and decreased mental alertness. In contrast, hyperthyroidism (too much thyroxine) is characterized by profuse perspiration, high body temperature, increased basal metabolic rate, high blood pressure, loss of weight, and irritability.
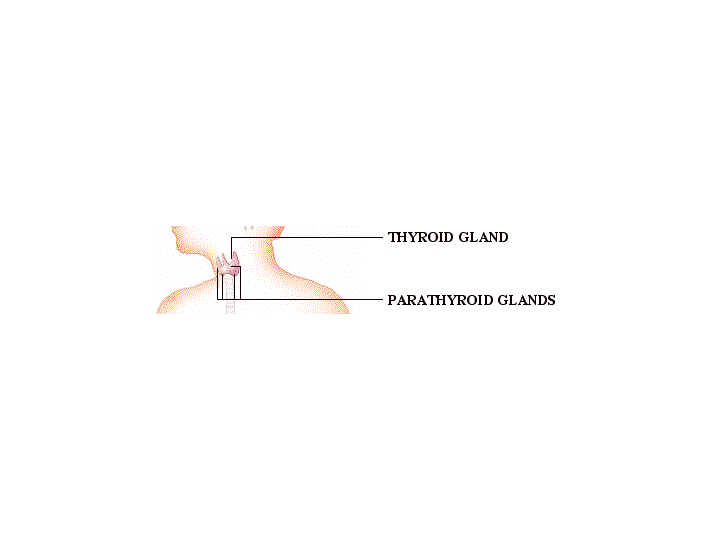
Parathyroid Glands
The parathyroid glands are small pealike organs located on the posterior surface of the thyroid. They secrete parathyroid hormone, which regulates the calcium and phosphate balance between the blood and other tissues. Increased parathyroid hormone increases bone resorption and elevates plasma calcium.
This animation (Audio - Important) describes the parathyroid gland.