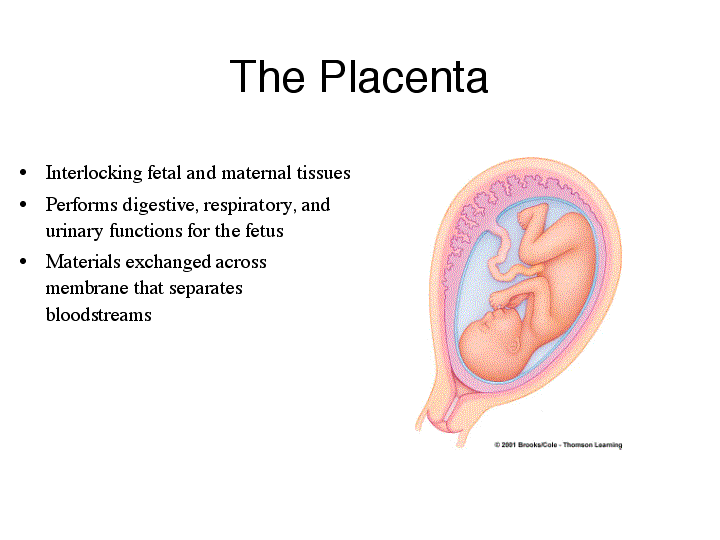

The placenta includes tissues of both the embryo and the mother. It is the site at which exchange of food, oxygen, waste, and water can take place.
In placental animals, there is no direct contact between the bloodstreams of the mother and the embryo. Transport is accomplished by diffusion and active transport between juxtaposed blood vessels of the mother and embryo. The umbilical cord that attaches the embryo to the placenta is composed completely of tissues of embryonic, not maternal origin. This cord contains the umbilical artery and vein.
This animation (Audio - Important) describes fetal development.
Take and look at the The Ovarian and Uterine Cycles Tutorial and the Gastrulation Tutorial.
REVIEW: Luteinizing hormone (LH) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)��
REVIEW: Ovulation occurs at which day of the ovarian cycle?� �
REVIEW: �At the end of the ovarian cycle, if a woman is not pregnant, the corpus luteum�
REVIEW: What is the function of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH)?��
REVIEW: The archenteron is the primitive _____ of an embryo and is completelly surrounded by _____.��
REVIEW: �From outside to inside, an embryo at the end of gastrulation has the following three embryonic tissue layers:�
REVIEW: Which of the following adult tissues or organs arises from the mesoderm?��
PREVIOUS
NEXT
LECTURE 7 INDEX
MAIN INDEX