Breathing
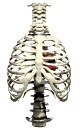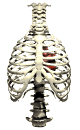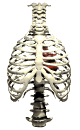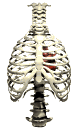 The lungs are found in a sealed cavity in the chest, bound by the ribs and chest wall and by the
muscular diaphragm on the bottom. The diaphragm is curved upward when released, and flattens when
contracted, expanding the chest cavity. Chest muscles move the ribs up and out, as the diaphragm
moves down. This creates both a larger chest cavity and a vacuum that forces air into the
respiratory passages (in a process known as
inhalation ). The reverse process decreases the size
of the chest cavity and forces air out of the lungs
( exhalation ). The breathing rate is controlled by a
part of the brain, the medulla oblongata, that monitors carbon dioxide content in the blood.
Excess CO2 in the blood stimulates the medulla to send messages to the rib muscles and
the diaphragm to increase the frequency of respiration.
The lungs are found in a sealed cavity in the chest, bound by the ribs and chest wall and by the
muscular diaphragm on the bottom. The diaphragm is curved upward when released, and flattens when
contracted, expanding the chest cavity. Chest muscles move the ribs up and out, as the diaphragm
moves down. This creates both a larger chest cavity and a vacuum that forces air into the
respiratory passages (in a process known as
inhalation ). The reverse process decreases the size
of the chest cavity and forces air out of the lungs
( exhalation ). The breathing rate is controlled by a
part of the brain, the medulla oblongata, that monitors carbon dioxide content in the blood.
Excess CO2 in the blood stimulates the medulla to send messages to the rib muscles and
the diaphragm to increase the frequency of respiration.
This animation (Audio - Important) describes
breathing.
PREVIOUS
NEXT
LECTURE 21 INDEX
MAIN INDEX
 The lungs are found in a sealed cavity in the chest, bound by the ribs and chest wall and by the
muscular diaphragm on the bottom. The diaphragm is curved upward when released, and flattens when
contracted, expanding the chest cavity. Chest muscles move the ribs up and out, as the diaphragm
moves down. This creates both a larger chest cavity and a vacuum that forces air into the
respiratory passages (in a process known as
inhalation ). The reverse process decreases the size
of the chest cavity and forces air out of the lungs
( exhalation ). The breathing rate is controlled by a
part of the brain, the medulla oblongata, that monitors carbon dioxide content in the blood.
Excess CO2 in the blood stimulates the medulla to send messages to the rib muscles and
the diaphragm to increase the frequency of respiration.
The lungs are found in a sealed cavity in the chest, bound by the ribs and chest wall and by the
muscular diaphragm on the bottom. The diaphragm is curved upward when released, and flattens when
contracted, expanding the chest cavity. Chest muscles move the ribs up and out, as the diaphragm
moves down. This creates both a larger chest cavity and a vacuum that forces air into the
respiratory passages (in a process known as
inhalation ). The reverse process decreases the size
of the chest cavity and forces air out of the lungs
( exhalation ). The breathing rate is controlled by a
part of the brain, the medulla oblongata, that monitors carbon dioxide content in the blood.
Excess CO2 in the blood stimulates the medulla to send messages to the rib muscles and
the diaphragm to increase the frequency of respiration.